
Optimalkan hasil Deteksi Objek dengan Non max suppression – merupakan algoritma yang dikembangkan untuk menghasilkan solusi ketika hasil object detection yang overlapping. Cerita ini dimulai ketika saya bekerja untuk sebuah project yang melibatkan proses object detection menggunakan deep learning yaitu untuk menentukan lokasi plate number pada sebuah vendor parking management. Setelah melakukan urusan data enginer yang bertugas melakukan labeling satu-persatu menggunakan format PASCALVOC

Dilanjutkan dengan algoritma deep learning yang didalamnya menggunakan selective search, proses pelatihan cukup lama hampir 28 jam, ternyata hasilnya kurang memuaskan yaitu seperti berikut

Malah terdeteksi 2 objek yang saling overlapping, hal ini harus dicarikan solusi yaitu dari Tomasz (Tom) Malisiewicz, Ph.D yang didalamnya menggunakan matlab yaitu Non max suppression serta artikel dari pyimagesearch mengenai non max supression. Perhatikan gambar berikut
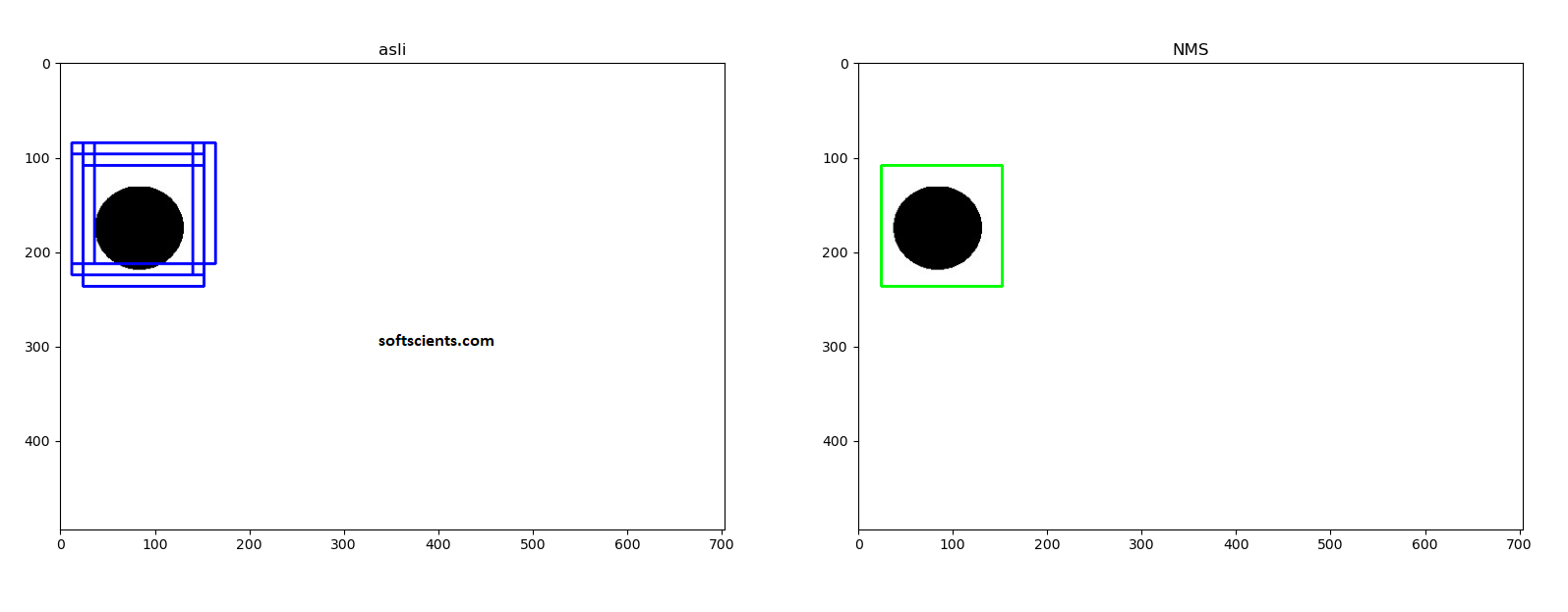
Optimalkan hasil Deteksi Objek dengan Non max suppression ketika saya terapkan maka hasilnya bagus seperti berikut

Bagaimana cara kerja Non max suppression
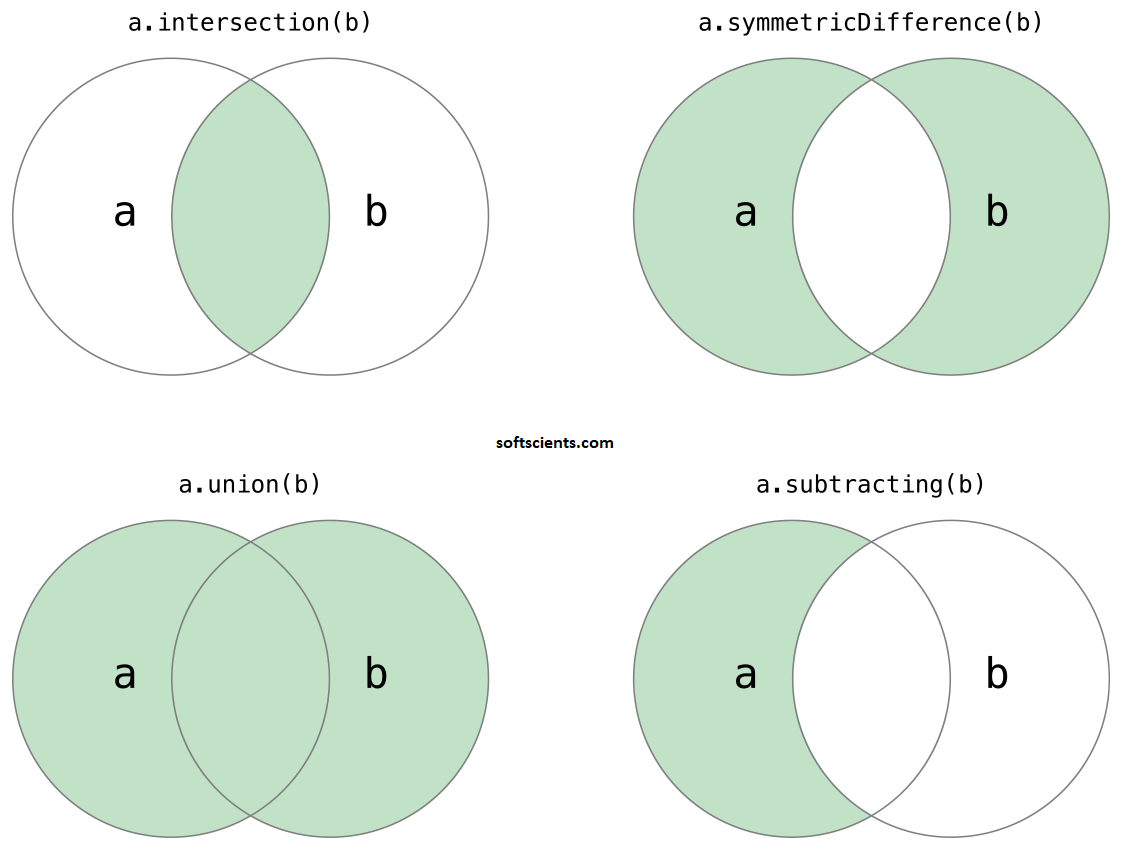
Cara kerja Optimalkan hasil Deteksi Objek dengan Non max suppression dengan melakukan operasi intersection, bila masih bingung, coba perhatikan ilustrasi berikut
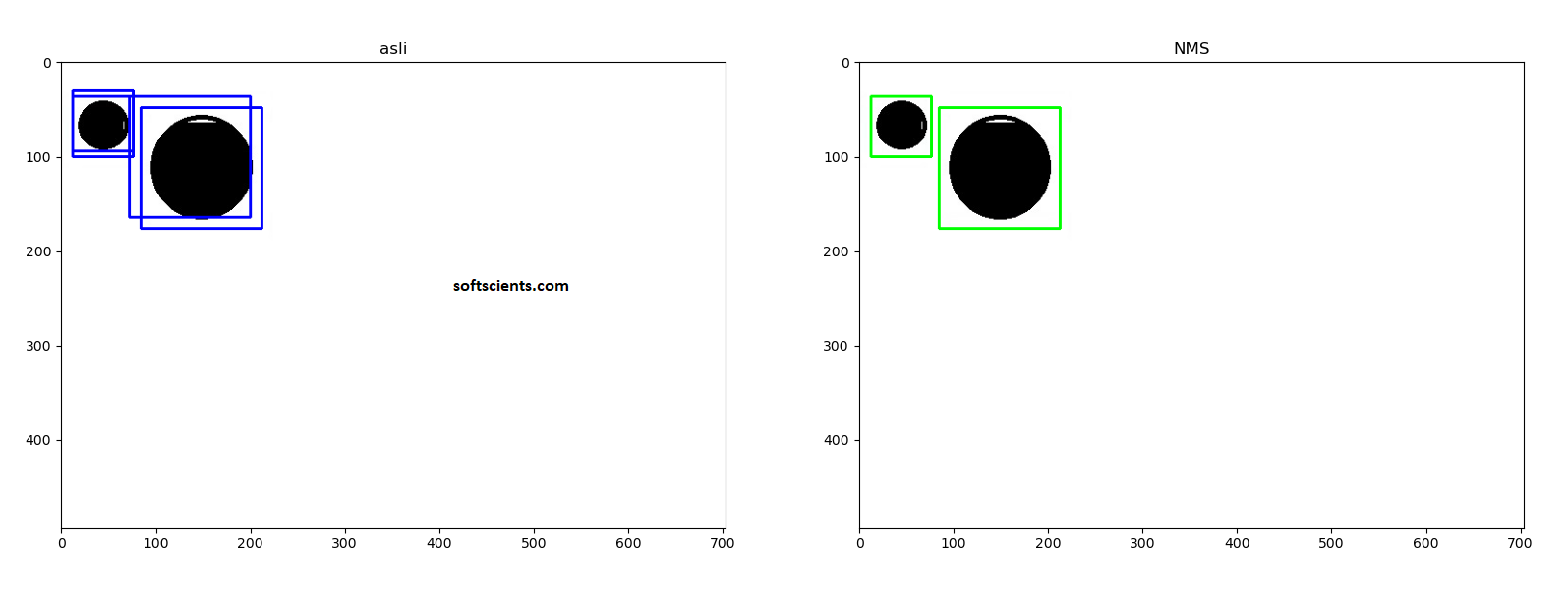
Dengan menggunakan Non max suppression maka overlapping bisa dihindarkan! Bilamana ada 2 objek, maka tidak akan mempengaruhi hasilnya seperti berikut
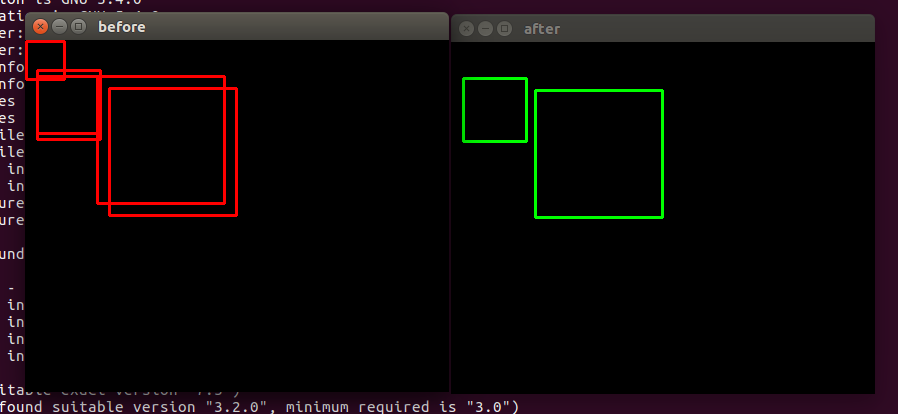
Adapun untuk kode Non max suppression yang saya gunakan dari PyImageSearch yaitu
# import the necessary packages
import numpy as np
# Felzenszwalb et al.
def non_max_suppression(boxes, overlapThresh):
# if there are no boxes, return an empty list
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
# initialize the list of picked indexes
pick = []
# grab the coordinates of the bounding boxes
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
# compute the area of the bounding boxes and sort the bounding
# boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
idxs = np.argsort(y2)
# keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes
# list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# grab the last index in the indexes list, add the index
# value to the list of picked indexes, then initialize
# the suppression list (i.e. indexes that will be deleted)
# using the last index
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
suppress = [last]
# loop over all indexes in the indexes list
for pos in range(0, last):
# grab the current index
j = idxs[pos]
# find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = max(x1[i], x1[j])
yy1 = max(y1[i], y1[j])
xx2 = min(x2[i], x2[j])
yy2 = min(y2[i], y2[j])
# compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = max(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = max(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# compute the ratio of overlap between the computed
# bounding box and the bounding box in the area list
overlap = float(w * h) / area[j]
# if there is sufficient overlap, suppress the
# current bounding box
if overlap > overlapThresh:
suppress.append(pos)
# delete all indexes from the index list that are in the
# suppression list
idxs = np.delete(idxs, suppress)
# return only the bounding boxes that were picked
return boxes[pick]
Cara menggunakannya seperti berikut
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2014/11/17/non-maximum-suppression-object-detection-python/
#https://github.com/rbgirshick/voc-dpm/blob/master/test/nms.m
# construct a list containing the images that will be examined
# along with their respective bounding boxes
images = [
("latihan/1.jpg", np.array([
(12, 84, 140, 212),
(24, 84, 152, 212),
(36, 84, 164, 212),
(12, 96, 140, 224),
(24, 96, 152, 224),
(24, 108, 152, 236)])),
("latihan/2.jpg", np.array([
(114, 60, 178, 124),
(120, 60, 184, 124),
(114, 66, 178, 130)])),
("latihan/3.jpg", np.array([
(12, 30, 76, 94),
(12, 36, 76, 100),
(72, 36, 200, 164),
(84, 48, 212, 176)]))]
# loop over the images
i = 1
for (imagePath, boundingBoxes) in images:
# load the image and clone it
print ("[x] %d initial bounding boxes" % (len(boundingBoxes)))
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
orig = image.copy()
# loop over the bounding boxes for each image and draw them
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in boundingBoxes:
cv2.rectangle(orig, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# perform non-maximum suppression on the bounding boxes
pick = non_max_suppression(boundingBoxes, 0.3)
print ("[x] after applying non-maximum, %d bounding boxes" % (len(pick)))
# loop over the picked bounding boxes and draw them
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in pick:
cv2.rectangle(image, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# display the images
#cv2.imshow("Original", orig)
#cv2.imshow("After NMS", image)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(1,2,1),plt.imshow(orig),plt.title("asli")
plt.subplot(1,2,2),plt.imshow(image),plt.title("NMS")
plt.show()
#cv2.waitKey(0)
i = i+1
Kode diatas sangat membantu sekali dalam deep machine learning dengan meningkatkan hasil akurasi deteksi objek yang saling overlapping.
Faster Non max suppression
Apabila kalian menggunakan pada video realtime yang boros CPU, kalian bisa membaca link berikut. Namun bagi kalian yang sedari awal menggunakan bahasa C++, bisa kunjungi link berikut . Tentu hasilnya lebih cepat dari Python
Ref:
https://learnopencv.com/non-maximum-suppression-theory-and-implementation-in-pytorch/
